Aggregate Demand. AD
-Shows the amount of real GDP that
the private, public, and foreign sector collectively desire to purchase
at each possible price level.
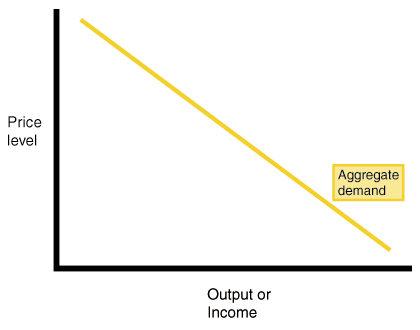
Three reasons AD is downward sloping.
Real Balances Effect
-when the price level is high households and businesses cannot afford to purchase as much output.
-when the price level is low households and businesses can afford to purchase more output.
Interest rate effect
-a higher price level increases the interest rate which tends to discourage investment
-a lower price level decreaes the interest rate which tends to encourage investment
Foreign purchases effect
-a higher price level increases the demand for relatively chaper imports
-a lower price level increases the foreign demand for relatively cheaper US exports
Shifts in Aggregate demand. AD
-There are two parts to a shift in AD
■
■
Increases in AD equals AD →

Consumption
-Household spending is affected by
■consumer wealth
● more wealth is more spending →
●less wealth is less spending ←
-Consumer expectations
● positive expectations is more spending →
●negative expectations is less spending ←
-Household indebtedness
●less debt is more spending →
●more debt is less spending ←
-Taxes
● less taxes is more spending →
● more taxes is less spending ←
Gross private investment
●Investment spending is sensitive to:
-The real interest rate
○Lower real interest rate is more investment
○higher real interest rate is less investment
-Expected Returns
○higher expected returns is more investment
○lower expected returns is less investments
○ expected returns are influenced by expectations of future
profitability, technology, degree of excess capacity, business taxes
Government spending
-More government spending AD shifts right
-Less government spending AD shifts left
Net Exports are sensitive to:
-Exchange rates (international value of $)
Strong $ is more imports and fewer exports is AD shifting to the left
Weak $ is fewer imports and more exports is AD shifting to right
-Relative Income
Strong foreign economies is more exports is AD shifted to the right
Weak foreign economies is less exports is AD shifted to the left
No comments:
Post a Comment