Money is any asset that can be used to purchase goods and services.
3 uses of money
- As a medium of exchange (using it to determine value- Unit of account is used to compare prices
- Store of value (where some people hide their money)
3 types of money
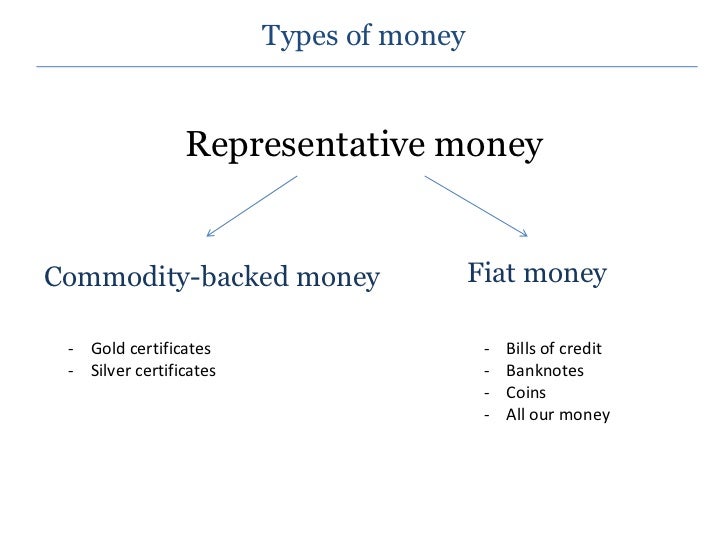
- Commodity money (has value within its self)- Representative money (represents something of value)
- Fiat money (money because Government says so)
6 characteristics of money
- Durability- Portability
- Divisible
- Uniformity
- Limited Supply
- Acceptability
Money Supply is the total value of financial assets available in the US economy.
M1 Money:
Involves Liquid Assets (easily converted to cash)- coins
- checks
- currency
- travel checks
M2 Money:
It is not as liquid as M1- savings account
- Money market account
3 purposes of financial institutions
- Store money
- Saved money
- Loan money

Two reasons why they loan money
- Credit cards- Mortgages
Four ways to save
- Savings account- Checking account
- Money market account
- Certificate of deposit
Loans: Banks operate on a fractional reserve system which means they keep a fraction of the funds and loan out the rest.
Interest rates
- Principle is amount of money borrowed
- Interest is the price paid for use of borrowed money
■ Simple Interest is paid on the principle
■ Compound interest is paid on the principle plus accumulated interest
Formula for simple interest:
I equals P times R times T over 100T equals I times 100 over P times R
P equals I times 100 over R times T
R equals I times 100 over P times T
Types of financial institutions
- Commercial bank- Savings and loans institutions
- Mutual savings bank
- Credit unions
- Finance Companies
Investment:
Redirecting resources. Consume now for the future.Financial Assests: are claims on property and income of borrower
Financial Intermediaries: institutions that channel funds from savers to borrowers. 3 purposes of financial intermediaries
- Share risks. Through diversification. Where spreading out investment to reduce risk.
- Provide information
- Liquidity (Returns) money investors above and beyond the sum of money that was initially invested
Bonds are loans that represent debt that the government or a corporation must repay to a investor. Generally low risk.
3 components of a bond
- Coupon rate is the interest rate that a bond insurer will pay to a bond holder- Maturity is the time in which payment to a bond holder is due
- Par value (principle) amount that an investor pays
- Yield is the annual rate of return on a bond if the bond were held to maturity
No comments:
Post a Comment